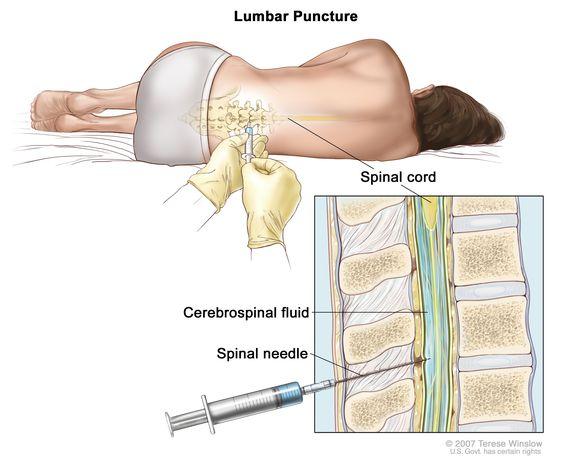
A lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, is a common medical procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the brain and spinal cord. It involves inserting a needle into the lower back to extract cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for testing. Performed by some of the best neurosurgeons in kolkata, this procedure is generally considered safe but can have side effects. Understanding these potential side effects helps patients know what to expect and how to manage them.
Common Side Effects
a. Headache
One of the most common side effects of a lumbar puncture is a post-lumbar puncture headache. This occurs due to the slight leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the puncture site, which can lead to a drop in pressure around the brain. The headache typically starts within a day or two after the procedure and can last for several days.
- Symptoms: The headache may worsen when sitting or standing and improve when lying down. It can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by nausea and neck stiffness.
- Management: Drinking fluids, especially those containing caffeine, resting, and lying down flat can help alleviate the headache. In more severe cases, a blood patch procedure may be required to seal the puncture site.
b. Back Pain
Some patients experience mild to moderate pain or discomfort in their lower back after a lumbar puncture. This is usually localized at the site of the needle insertion and tends to resolve within a few days.
- Symptoms: Pain at the puncture site, occasional muscle spasms, or stiffness in the lower back.
- Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage the discomfort. Resting and avoiding strenuous activities can also speed up recovery.
c. Numbness or Tingling
In rare cases, patients may experience temporary numbness or tingling in their legs or lower back after a lumbar puncture. This is usually due to irritation of the nerves during the procedure and tends to resolve on its own.
- Symptoms: Sensations of numbness, tingling, or weakness in the lower body.
- Management: If the symptoms persist or worsen, it's important to contact a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
a. Infection
Though rare, there is a small risk of infection at the puncture site, especially if proper sterilization techniques are not followed.
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, warmth, or pus at the puncture site, along with fever or chills.
- Management: In case of suspected infection, a doctor may prescribe antibiotics. It’s important to report any signs of infection immediately to prevent complications.
b. Bleeding
Bleeding is another uncommon side effect of lumbar punctures. It may occur in patients with clotting disorders or those taking blood-thinning medications.
- Symptoms: Bruising, swelling, or increased pain at the puncture site, along with dizziness or weakness.
- Management: Doctors usually perform blood tests before the procedure to check for clotting issues. Any signs of abnormal bleeding should be addressed promptly by a healthcare provider.
c. Herniation (Very Rare)
In extremely rare cases, a lumbar puncture can lead to brain herniation in patients with increased intracranial pressure. This is a life-threatening condition where brain tissue is pushed down toward the spinal cord.
- Symptoms: Severe headache, changes in consciousness, difficulty breathing, or seizures.
- Management: Doctors take precautions by performing brain imaging before the lumbar puncture to rule out this risk.
How to Reduce Side Effects
There are steps patients can take to minimize the side effects of a lumbar puncture:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids before and after the procedure helps reduce the likelihood of post-lumbar puncture headaches.
- Rest: Taking it easy for at least 24 hours after the procedure can help reduce discomfort and speed up recovery.
- Report Symptoms: Informing your doctor of any unusual symptoms, such as severe headaches or signs of infection, ensures prompt treatment.
Conclusion
A lumbar puncture is a safe and valuable diagnostic tool, but like any medical procedure, it carries potential side effects. The most common issues are headaches, back pain, and, in rare cases, infections or bleeding. Understanding these risks and how to manage them can help patients navigate the procedure with confidence. Always follow the advice of healthcare providers to minimize discomfort and ensure a smooth recovery,

